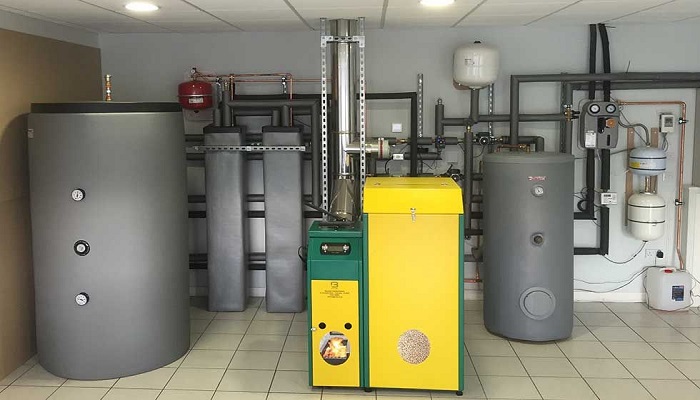
The UK is at present facing concerns with regard to energy security, and because of this, an industry report has highlighted the potential of hot water cylinders in helping to balance the demand on the electrical grid.
The Hot Water Association- HWA report, titled Connected Homes, examines the possibility of making use of hot water cylinders as thermal stores when it comes to grid electricity. Apparently, this methodology looks to enhance resilience during peak periods.
By way of connecting nine million cylinders across the UK homes via smart controls as well as utilizing them like batteries, the National Grid could possibly go on to access 23GWh of energy storage, which, by the way, is equivalent to almost half of the energy consumed every day in the UK.
It is well to be noted that the introduction of technologies like heat pumps, which happen to require hot water cylinders, could go on to potentially raise this number by 36%, thereby resulting in an energy capability of 40GWh. So as to harness the energy storage capacity in an effective way, it is essential to have smart functionalities within the cylinders, which can be achieved by either retrofitting existing cylinders by way of smart controls or installing new smart cylinders with gas boilers or heat pumps.
Apparently, it is the heating engineers who will go on to play a crucial role when it comes to the execution of this idea, as underscored by Kevin Lowe, who happens to be the Technical Manager at the HWA. He went on to state that hot water cylinders have prominent potential within the energy sector, and there is a requirement for efforts so as to maximize this opportunity. Installers throughout the UK who happen to be installing as well as maintaining cylinders across homes can play a crucial role in this process. The report stresses the importance of these installers in making sure both existing as well as new cylinders are aptly connected.
The HWA reports emphasize the significance of policy direction in giving to the homeowners to adopt connected thermal storage across UK homes. It is indeed critical to implement measures so as to prevent individuals from eliminating the cylinder in their hot water system, since doing so could lead to a rise in the number of UK cylinders to expand capacity.
This report not only suggests offering incentives so as to encourage more people to put in smart cylinders as well as retrofit controls to existing cylinders, but at the same time outlines the next steps for elevating the adoption of these measures. One way to elevate SAP and EPC ratings in new construction is by making sure to optimize smart controls and cylinders. Apart from this, reducing taxes and levies on off-peak electricity can raise the value, which is derived from storing energy in a cylinder.
Lowe further says that the critical factor in bringing this project to its actual might is gaining the support of homeowners. Hence, it is imperative that policy directions be designed to encourage the embracement of smart hot water storage. Homeowners may require financial support to make it worthwhile when installing a cylinder with a novel heat pump or fitting controls to one that’s existing.
In addition, homeowners should also be well versed in the advantages of thermal storage within their homes, which may go on to discourage them from removing their presently used hot water cylinder. To accomplish the potential 40GWh of energy storage in the UK as defined by the study, it is critical for industry, government, as well as installers to partner and educate homeowners about these advantages.