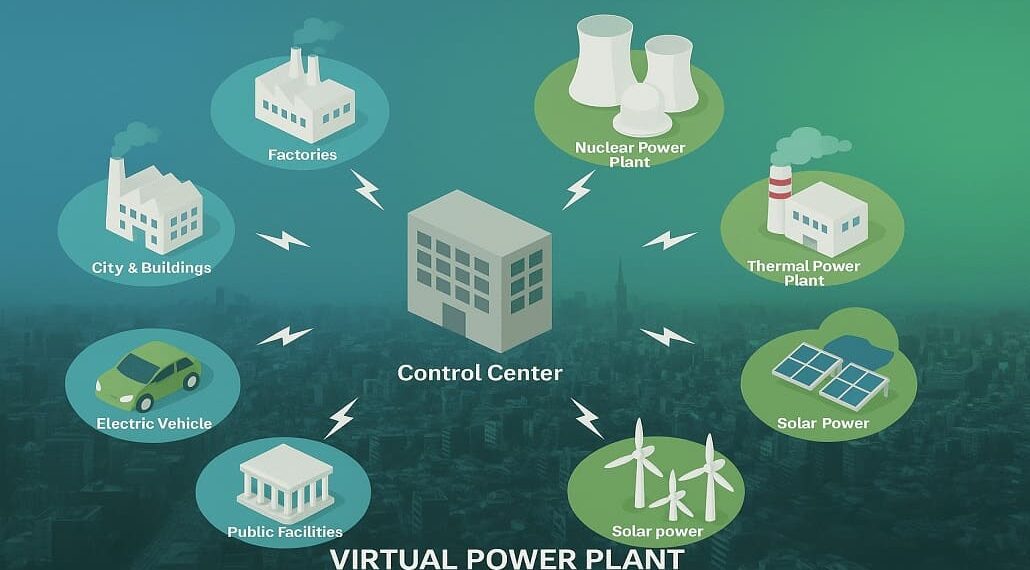
As the global energy landscape undergoes a profound transformation, Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) are emerging as a groundbreaking solution to decentralize energy management and enhance grid stability. VPPs are a technological marvel that solve these problems through the aggregation of distributed energy resources (DER) to form a cohesive, virtual Power plant capable of acting like a complete electricity generation capability.
In essence, VPPs use the combined power of decentralised energy systems including rooftop solar panels, energy storage devices, electric vehicles, and demand-response systems. These networks use modern software, real-time data analysis, and intelligent control systems to optimise energy generation, distribution, and consumption, allowing for more effective and sustainable management. But as energy systems increasingly become smart and connected, VPPs are ready to change the ways electricity is generated, controlled, accepted, and consumed.
The Concept of Virtual Power Plants
A virtual power plant is not a physical infrastructure but rather a sophisticated network that aggregates small, decentralized energy resources and collectively manages them to function as a unified energy system. Such resources can be renewable energy installations in the form of solar panels and wind turbines, energy storage units and dynamic demand-response assets. Cloud platforms and artificial intelligence (AI) technology are leveraged to aggregate such resources, where real-time energy supply and demand optimization takes place.
VPPs work in a decentralised way, while standard power plants depend on large-scale infrastructure and centralised generation. This not only makes the grid more flexible, but it also cuts down on fossil fuel use by putting renewable energy and distributed production at the top of the list. Consequently, VPPs are being adopted as a scalable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly energy management solution over conventional means.
The Role of VPPs in Decentralized Energy Management
Decentralization is a defining feature of modern energy systems. As more homes, businesses, and communities produce their own electricity with rooftop solar panels and other renewable technologies, the old top-down system of energy management is sounding less relevant. VPPs provide an ecosystem for decentralized resources to work together and pool their contributions to the power grid in the face of this paradigm shift.
One of the most significant contributions of VPPs is their ability to balance supply and demand dynamically. Electricity generated from renewable sources like wind or solar is inherently variable, making it difficult to match generation to demand. Demand response programs are powered by VPPs that use machine learning and real-time data analytics to predict bird energy output and consumption patterns. Following are some important advantages of Monroe Energy to the hosts. This predictive capability allows for precise adjustments in energy flow, ensuring supply meets demand even under fluctuating conditions.
Furthermore, VPPs enhance grid resilience by distributing energy generation across multiple decentralized assets. In traditional, centralized systems, a failure at a single power plant can lead to widespread outages. In contrast, the distributed nature of VPPs minimizes the impact of individual failures, ensuring a more robust and reliable energy supply.
The Integration of Renewable Energy
The global transition towards sustainability and higher penetration of renewables into energy systems are driving the adoption of VPPs. Renewables such as solar and wind play a crucial role in cutting down on carbon emissions, but their non-constant nature can make it difficult to maintain grid reliability and stability. VPPs spatially enable the integration of renewables in energy production, overcoming these limitations.
For instance, a VPP can aggregate energy generated by thousands of rooftop solar installations and manage it collectively, smoothing out fluctuations caused by weather variations. By combining renewable energy generation with energy storage systems such as batteries, VPPs create a buffer that ensures a steady energy supply during times of low generation.
This includes making renewable energy generation more viable at scale (both for the grid and the community level. VPPs allow utilities and grid operators to take advantage of the growing prevalence of renewables while maintaining system reliability, and local communities enjoy lower energy costs and reduced dependence on traditional grid energy.
Advanced Technologies Powering VPPs
The success of virtual power plants depends on advanced technologies that allow for the integration, monitoring, and optimization of distributed energy resources. Central to these systems are IoT (Internet of Things) devices, which collect real-time data from energy assets. These devices provide granular insights into energy generation, consumption, and storage, creating a comprehensive picture of the system’s performance.
AI (artificial intelligence) and ML (machine learning) play a pivotal role in VPP operations. These technologies analyze vast quantities of data to forecast demand patterns, optimise energy dispatch and detect potential problems before they occur. For example, AI can forecast peak demand periods and strategically allocate energy resources to meet demand efficiently, reducing costs and minimizing energy waste.
Blockchain tech is indeed another innovation that adds to VPPs functionality. Blockchain, in the implementation of VPP (Virtual Power Plant), enables peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading within the distributed energy-system unit by providing a secure, decentralized platform for the exchange of energy. This not only empowers consumers to become energy prosumers but also creates new revenue streams and promotes local energy sustainability.
Benefits of Virtual Power Plants
Adopting VPPs also provides numerous advantages, both from a business standpoint and environmental perspectives. Economically speaking, virtual power plants lower the cost of energy by using existing resources in the most efficient way and reducing wasted potential. These systems, known as VPPs, aggregate small-scale resources to allow utilities and grid operators to forgo significant capital investments in new infrastructure by leveraging existing assets.
On the environmental side, VPPs contribute to the clean energy transition globally by emphasizing renewables and helping with greenhouse gas (GHG) emission mitigation. VPPs facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind into power systems, helping to decarbonize energy systems and meet climate targets.
Operationally, VPPs enhance grid stability, resilience, and flexibility. Their ability to balance supply and demand in real-time reduces the risk of outages and ensures reliable energy access even during peak demand periods. Additionally, VPPs enable faster recovery from disruptions, as their decentralized nature allows for localized responses to grid issues.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
A few notable successful VPP implementations illustrate their transformative potential. For instance, in Germany, a medium-scale VPP comprises 20,000 distributed energy assets, including solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems. Not only do this network supplies reliable energy to grid as they also participate in energy markets by providing balancing services.
In Australia, VPPs enable homeowners and companies to become active players in the energy market. By connecting rooftop solar arrays and home batteries, these systems let customers to sell excess energy back to the grid, resulting in a more fair and sustainable energy ecology.
The United States is also seeing an increase in VPP use, with utilities using the technology to integrate renewables and modernise infrastructure. These efforts are especially significant in states like California, which has one of the highest renewable energy penetration rates in the country.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its numerous benefits, broad use of VPPs is not without hurdles. Challenges include regulatory impediments, difficult integration of energy assets, and cybersecurity issues. Experts from the government and commercial sector must collaborate to address these concerns and create an atmosphere that supports VPP growth.
The outlook for VPPs, though, is still overwhelmingly positive. The current global market for virtual power plants (VPPs) is projected to grow with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 20% over the next ten years, as the combination of more renewables on the grid, better technology and favorable policy conditions bring such solutions into widespread use. With the increasing focus on grid modernization worldwide, VPP’s will undoubtedly play a critical role in the future of energy management.
Conclusion
The arrival of Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) is reshaping energy management by decentralizing power generation, optimizing the use of resources, and strengthening the resilience of the grid. VPPs provide the solution to modern-day energy challenges through the aggregation of distributed energy resources (DERs) using sophisticated technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, which can ultimately provide a sustainable, economical, and efficient method of energy delivery as well as consumption.
As the energy industry evolves, VPPs will play an important role in integrating renewables, empowering communities, and pave the path for a cleaner, more resilient energy future. Digital technologies have the potential to change energy systems through their ability to organise decentralised assets. Virtual power plants have the potential to revolutionise energy management with appropriate regulations, investments, and technical advancements.